Sometimes preferred stock is considered an asset, while other times, it’s considered a liability. This impacts the debt-to-equity ratio and can throw off your personal analysis of a company if you are not aware of how a particular analyst came up with the debt-to-equity ratio. If a company has a negative D/E ratio, this means that it has negative shareholder equity. In most cases, this would be considered a sign of high risk and an incentive to seek bankruptcy protection. On the other hand, the typically steady preferred dividend, par value, and liquidation rights make preferred shares look more like debt.
How to Make Serious Money: Digital Real Estate for Beginners
The D/E ratio also gives analysts and investors an idea of how much risk a company is taking on by using debt to finance its operations and growth. Although debt financing is generally a cheaper way to finance a company’s operations, there comes a tipping point where equity financing becomes a cheaper and more attractive option. A higher D/E ratio means that the company has been aggressive in its growth and is using more debt financing than equity financing.
What are gearing ratios and how does the D/E ratio fit in?
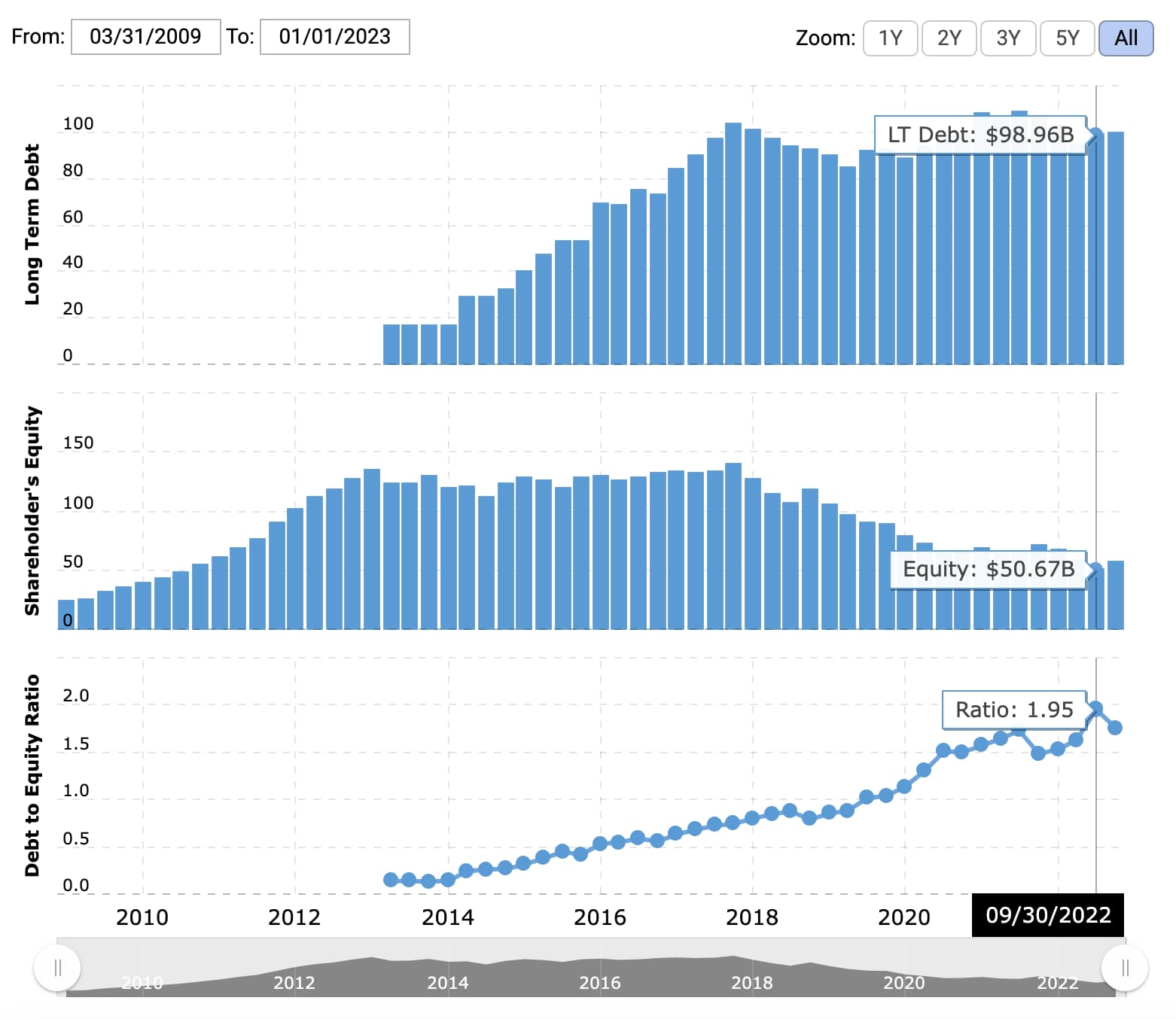
In this guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know about the D/E ratio to help you make better financial decisions. There is no universally agreed upon “ideal” D/E ratio, though generally, investors want it to be 2 or lower. For this reason, it’s important to understand the norms for the industries you’re looking to invest in, and, as above, dig into the larger context when assessing the D/E ratio.
What is a good debt-to-equity ratio?
At the same time, leverage is an important tool that companies use to grow, and many businesses find sustainable uses for debt. To determine the debt to equity ratio for Company C, we have to calculate the total liabilities and total equity, and then divide the two. Despite being a good measure of a company’s financial health, debt to equity ratio has some limitations that affect its effectiveness. Financial leverage simply refers to the use of external financing (debt) to acquire assets.
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
- Looking at the balance sheet for the 2023 fiscal year, Apple had total liabilities of $290 billion and total shareholders’ equity of $62 billion.
- However, since they have high cash flows, paying off debt happens quickly and does not pose a huge risk to the company.
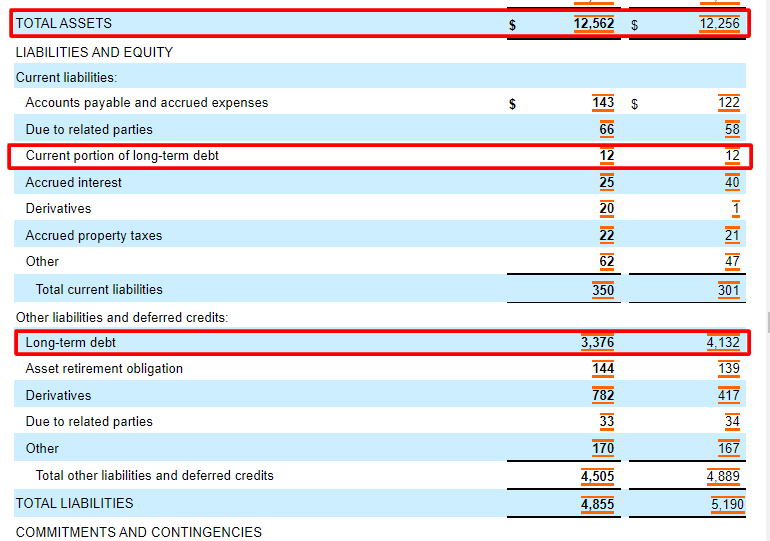
- This second classification of short-term debt is carved out of long-term debt and is reclassified as a current liability called current portion of long-term debt (or a similar name).
- There are various companies that rely on debt financing to grow their business.
The formula for calculating the debt-to-equity ratio (D/E) is equal to the total debt divided by total shareholders equity. What counts as a “good” debt-to-equity (D/E) ratio will depend on the nature of the business and its industry. Generally speaking, a D/E ratio below 1 would be seen as relatively safe, whereas values of 2 or higher might be considered risky. Companies in some industries, such as utilities, consumer staples, and banking, typically have relatively high D/E ratios. Perhaps 53.6% isn’t so bad after all when you consider that the industry average was about 75%.
Cons of Debt Ratio
A company’s total liabilities are the aggregate of all its financial obligations to creditors over a specific period of time, and typically include short term and long term liabilities and other liabilities. The D/E ratio is arguably one of the most vital metrics to evaluate a company’s financial leverage as it determines how much debt or equity a firm uses to finance its operations. When finding the D/E ratio of a company, it’s vital to compare the ratios of other companies within the same industry for a better idea of how they’re performing. The debt-to-equity ratio (D/E) is a ratio that measures an organization’s financial leverage by dividing total debt by shareholder’s equity. This ratio helps lenders, investors, and leaders of companies evaluate risk levels and determine whether a company is over-leveraged or under-leveraged.
A high ratio indicates that a company may be at risk of default on its loans if interest rates suddenly rise. A ratio below 1 means that a greater portion of a company’s assets is funded by equity. A low debt to equity the best 10 excel bookkeeping templates for free wps office academy ratio, on the other hand, means that the company is highly dependent on shareholder investment to finance its growth. A high debt to equity ratio means that a company is highly dependent on debt to finance its growth.
Using excel or another spreadsheet to calculate the D/E is relatively straightforward. First, using the company balance sheet, pull the total debt amount and the total shareholder equity amount, and enter these numbers into adjacent cells (e.g. E2 and E3). The term “leverage” reflects the hope that the company will be able to use a relatively small amount of debt to boost its growth and earnings. Wise use of debt can help companies build a good reputation with creditors, which, in turn, will allow them to borrow more money for potential future growth. All you need to calculate shareholder’s equity is the number of total assets in your company and the number of total liabilities, which you calculated in Step 1. From the above, we can calculate our company’s current assets as $195m and total assets as $295m in the first year of the forecast – and on the other side, $120m in total debt in the same period.
0 Comments